-
Research Article

-
A study on improving the computational efficiency of debris flow numerical models using dynamic grid activation method
동적 격자 활성화 기법을 활용한 토석류 수치모형의 계산 효율 향상 연구
-
Taeun Kang, Minseok Kim, Hyunuk An, Seungsoo Lee
강태운, 김민석, 안현욱, 이승수
- Due to the recent increase in the frequency of localized heavy rainfall, the occurrence of landslides and debris flows has been rising …
최근 빈번한 국지성 폭우로 인한 산사태 및 토석류의 발생 빈도가 전국적으로 증가함에 따라, 이에 대한 정확한 예측 및 선제적 대응 방안 마련의 …
- Due to the recent increase in the frequency of localized heavy rainfall, the occurrence of landslides and debris flows has been rising nationwide, highlighting the need for accurate prediction and proactive response measures. To address this, scenario-based predictions for hazard mapping are essential, and a balance between computational efficiency and spatial resolution must be achieved. This study proposes a Dynamic Grid Activation technique that selectively activates computational cells based on the presence or potential of active flow during simulation. By excluding areas unrelated to debris flow, unnecessary computations are significantly reduced. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, four simulation scenarios were compared: (1) full-domain computation, (2) full-domain parallel computation, (3) dynamic grid activation based on active flow, and (4) dynamic grid activation combined with parallel computation. These scenarios were applied to an actual debris flow event for comparison. Results show that the dynamic activation with parallel computation achieved identical simulation accuracy to the conventional method while improving computation speed by up to 3.49 times. Therefore, the proposed method is expected to significantly enhance the computational efficiency of debris flow models, enabling faster prediction and more effective parameter calibration.
- COLLAPSE
최근 빈번한 국지성 폭우로 인한 산사태 및 토석류의 발생 빈도가 전국적으로 증가함에 따라, 이에 대한 정확한 예측 및 선제적 대응 방안 마련의 필요성이 커지고 있다. 이를 위해서는 다양한 시나리오 기반의 사전 모의를 통한 위험지도 작성이 요구되며, 예측 모형의 계산 효율성과 해상도 간의 균형 확보가 중요하다. 본 연구에서는 활성흐름 기준으로 계산 도메인을 동적으로 활성화하는 동적 격자 활성화 기법을 제안하고, 해당 기법의 계산 효율 향상 효과를 분석하였다. 제안된 방법은 활성흐름이 존재하거나 거동 가능성이 있는 격자만을 계산에 포함하고, 토석류 이외 지역은 제외함으로써 불필요한 연산을 줄인다. 이를 검증하기 위해 (1) 전체 도메인을 계산하는 기존 방식, (2) 전체 도메인을 병렬 계산하는 방식, (3) 모의 중 활성흐름 분포에 따라 격자를 동적으로 활성화하는 방식, (4) 모의 중 활성흐름 분포에 따라 격자를 동적으로 활성화하는 동시에 병렬계산을 수행하는 4 가지 주요 시나리오를 혼합해 실제 토석류 피해지역에 적용하여 비교‧분석하였다. 그 결과, 모의 중 활성흐름 분포에 따라 격자를 동적으로 활성화하는 방식과 병렬계산을 병행한 방식이 기존 방식의 모의결과와 값이 동일하면서도 최대 3.49배 정도 계산 속도가 증가한 것으로 나타났다. 따라서 본 연구에서 개발한 동적 격자 활성화 기법을 토석류 해석 모형에 적용시 계산 효율을 실질적으로 향상시켜 빠른 예측과 매개변수 보정 등을 수행할 수 있을 것으로 기대한다.
-
A study on improving the computational efficiency of debris flow numerical models using dynamic grid activation method
-
Research Article
-
Assessmengt of river sediment discharge using acoustic backscatter in moving-boat ADCP
이동식 ADCP 초음파 산란도를 활용한 하천 유사량 산정
-
Jeong, BoseongㆍKim, DongsuㆍSon, GeunsuㆍRoh, YoungsinㆍChoi, Suin
정보성, 김동수, 손근수, 노영신, 최수인
- This study presented a method for quantitatively estimating suspended-sediment load in rivers using acoustic backscatter data obtained from a moving-boat ADCP (Acoustic …
본 연구는 이동식 ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler)의 초음파 산란도 자료를 활용하여 하천 부유사량을 정량적으로 산정하는 방법을 제시하였다. 기존 채집기 방식이 갖는 …
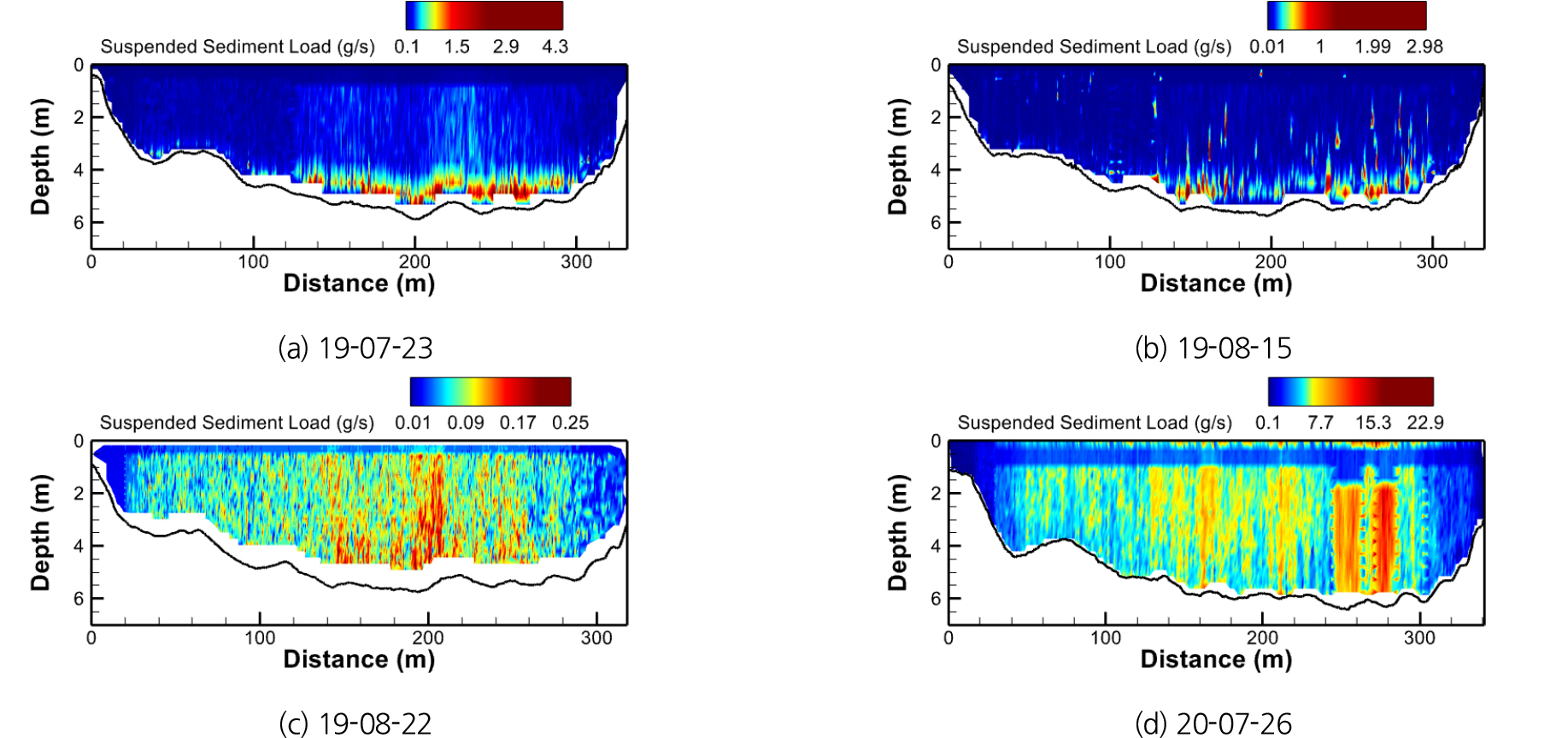
- This study presented a method for quantitatively estimating suspended-sediment load in rivers using acoustic backscatter data obtained from a moving-boat ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler). To overcome the spatial limitations of conventional physical sampling methods, an advanced algorithm was applied to separate fine and coarse suspended sediments based on a threshold particle diameter of 0.062 mm, along with acoustic corrections for water absorption, particle attenuation, and beam spreading. Field measurements were conducted at the “Hoguk Bridge” section of the Nakdong River using RiverPro (1200 kHz) and RiverRay (600 kHz) ADCPs, and the results were compared with D-74 physical samples collected at the same location. The analysis showed that fine sediments were uniformly distributed across the cross-section, whereas coarse sediments tended to concentrate near the riverbed. The ADCP-based suspended-sediment load estimates exhibited less than 10% deviation from the measured values, demonstrating their quantitative accuracy and reliability. These findings confirm that the ADCP-based method offers an effective alternative to traditional sediment sampling approaches.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 이동식 ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler)의 초음파 산란도 자료를 활용하여 하천 부유사량을 정량적으로 산정하는 방법을 제시하였다. 기존 채집기 방식이 갖는 공간적 한계를 보완하기 위해, 입경 0.062 mm를 기준으로 세립질과 조립질 부유사를 분리하는 최신 알고리즘을 적용하고, 수중 흡수, 입자 감쇠, 빔 확산 등의 음향 보정을 수행하였다. 낙동강 칠곡군 ‘호국의 다리’ 구간에서 RiverPro (1200 kHz)와 RiverRay (600 kHz)를 활용하여 측정된 ADCP 자료를, 동일 지점에서 확보한 D-74 채집기 실측 시료와 비교하였다. 분석 결과, 세립질 부유사는 단면 전역에 균일하게 분포한 반면, 조립질 부유사는 하상 부근에 집중되는 경향을 보였으며, ADCP 기반 부유사량 산정값은 실측값과 10% 이내의 오차를 보여 정량적 정확도와 신뢰성을 입증하였다. 이를 통해 ADCP 기반 부유사 산정 기법이 재래식 계측 방식을 대체할 수 있는 효과적인 수단임을 확인하였다.
-
Assessmengt of river sediment discharge using acoustic backscatter in moving-boat ADCP
-
Research Article
-
Development of a cluster analysis-based heavy rainfall damage prediction functions and their performance comparison
군집분석 기반 호우피해예측 함수 개발 및 예측 성능 비교
-
Yoo, Jin GyeongㆍJung, DonghwiㆍYoo, Do Guen
유진경, 정동휘, 유도근
- According to the Ministry of the Interior and Safety's Disaster Yearbook, heavy rain continues to cause damage in South Korea every year, …
행정안전부 재해연보에 따르면 우리나라에서는 매년 호우로 인한 피해가 지속되며, 자연재해 중 재산피해 비중이 가장 높다. 이에 본 연구는 강우 규모, 지리적 위치, …
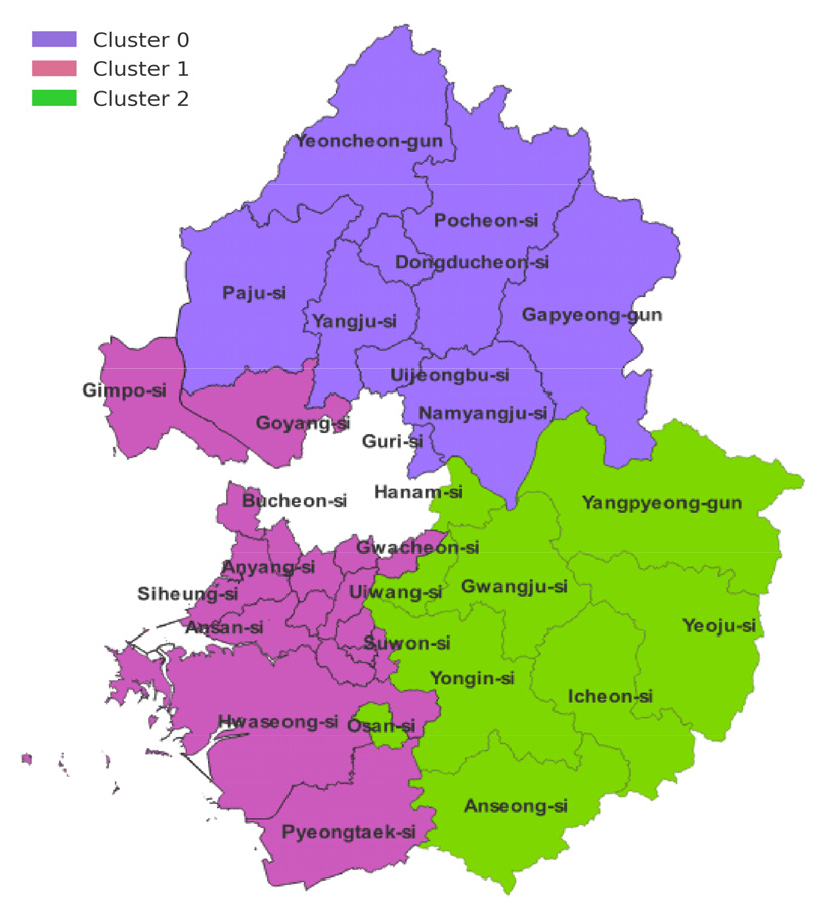
- According to the Ministry of the Interior and Safety's Disaster Yearbook, heavy rain continues to cause damage in South Korea every year, and property damage accounts for the largest proportion of natural disasters. Therefore, this study classified local governments in Gyeonggi Province using K-means clustering analysis, considering regional characteristics such as rainfall intensity, geographic location, and damage scale. Based on this, a heavy rain damage prediction function was developed. The analysis focused on local governments in Gyeonggi-do, using data from 2013 to 2023. Predictor variables consisted of meteorological and socioeconomic factors. Decision Tree Bagging (DT-Bagging) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models, which have demonstrated excellent predictive performance in previous studies, were used as prediction models. Mean Square Error (MSE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), and Normalized Root Mean Squared Error (NRMSE) were used to compare the predictive performance of the two models. The prediction performance comparison results showed that the DT-Bagging function achieved a 97.2% improvement over the LSTM function. Therefore, this study is expected to contribute to the establishment of a precise flood damage prediction and disaster management system based on the characteristics of local governments.
- COLLAPSE
행정안전부 재해연보에 따르면 우리나라에서는 매년 호우로 인한 피해가 지속되며, 자연재해 중 재산피해 비중이 가장 높다. 이에 본 연구는 강우 규모, 지리적 위치, 피해 규모 등과 같은 지역적 특성을 고려하여 군집분석(K-means)을 통해 경기도 내 지자체를 분류하고, 이를 바탕으로 호우피해예측 함수를 개발하였다. 분석 대상은 경기도 내 지자체이며, 2013년부터 2023년까지의 데이터를 활용하였다. 예측 변수는 기상요소와 사회·경제적 요인으로 구성하였다. 예측 모델로는 선행연구에서 예측 성능이 우수했던 의사결정나무 기반 배깅(Decision Tree Bagging, DT-Bagging)과 장단기메모리(Long Short-Term Memory, LSTM)을 적용하였다. 두 가지 모델의 예측 성능 비교를 위해 평균제곱오차(Mean Square Error, MSE), 평균제곱근오차(Root Mean Square Error, RMSE), 정규화 평균제곱근오차(Normalized Root Mean Squared Error, NRMSE)를 사용하였다. 예측 성능 비교 결과, DT-Bagging 함수가 LSTM 함수 대비 97.2%의 향상률을 보였다. 따라서 본 연구는 지자체 특성에 기반한 정밀한 호우피해예측과 재난관리 체계 구축에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Development of a cluster analysis-based heavy rainfall damage prediction functions and their performance comparison
-
Research Article
-
Estimating time of concentration by DMCA method
DMCA 기법을 이용한 도달시간 추정
-
Yoo, Ji SungㆍKim, Sang Ug
유지성, 김상욱
- The time of concentration (Tc) is a critical parameter in the planning and design of hydraulic structures. Conventional methods such …
도달시간(time of concentration, Tc)은 수공구조물의 계획 및 설계에서 중요한 인자이다. 현재 도달시간은 등시간선을 이용한 물리적 방법과 지형적 자료를 이용한 회귀분석 …
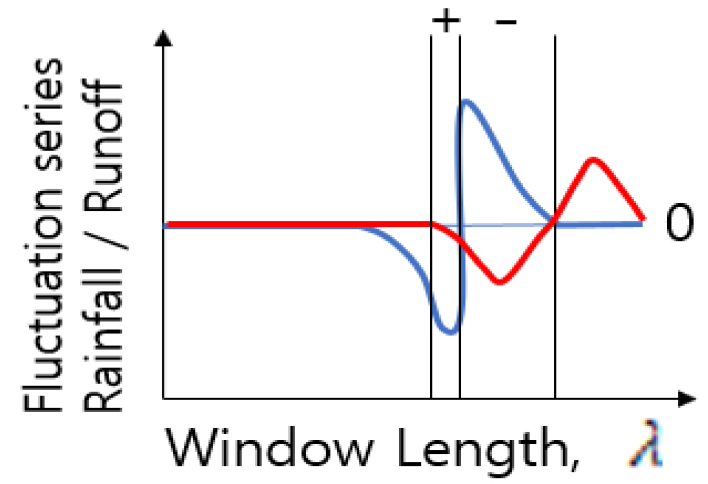
- The time of concentration (Tc) is a critical parameter in the planning and design of hydraulic structures. Conventional methods such as physical methods with isochrones and regression based on topographic data, usually produced results with significant uncertainty. Therefore, The objective of this study is to introduce the newly developed method and to test its applicability to a domestic watershed. This study introduced the Detrending Moving-average Cross-correlation Analysis (DMCA) method, which can estimate Tc directly from observed rainfall and runoff data. Application with six conventional formulas to the Soyangang Dam basin yielded Tc values ranging from 10.20 hr to 46.24 hr, highlighting substantial uncertainty. DMCA method showed the reduced uncertainty as data length increased, with Tc estimated at 13.00 hr when the full data set was used. This study has certain limitations, including the use of a single watershed and rainfall station, as well as subjective screening of rainfall and runoff data. Future research should extend the analysis to a larger number of gauged basins to identify watershed-specific characteristics of existing Tc formulas and to propose appropriate Tc ranges. Also the DMCA method may provide an alternative approach for Tc estimation in ungauged basins.
- COLLAPSE
도달시간(time of concentration, Tc)은 수공구조물의 계획 및 설계에서 중요한 인자이다. 현재 도달시간은 등시간선을 이용한 물리적 방법과 지형적 자료를 이용한 회귀분석 공식에 의해 주로 추정되고 있다. 이 같은 방식에 의한 도달시간 추정결과는 불확실성이 매우 크므로 실무적용에 어려움이 있다는 점이 기존 연구자들에 의해 제시된 바 있다. 따라서 이 연구에서는 이와 같은 문제점을 개선하기 위하여 여러 가정에 기반한 도달시간 산정방식이 아닌 관측된 강우와 유출자료만을 이용하여 도달시간을 추정할 수 있는 DMCA (Detrending Moving-average Cross-correlation Analysis) 기법을 소개하였다. 소양강 중권역에 기존의 6가지 도달시간 공식을 사용한 결과, 도달시간이 최소 10.20 hr부터 최대 46.24 hr로 산정되어 불확실성의 범위가 매우 넓음을 확인하였다. DMCA 기법을 사용한 결과는 자료의 길이가 증가됨에 따라 불확실성이 범위가 감소함을 확인하였으며, 모든 자료를 사용한 경우의 도달시간은 13.00 hr으로 산정되었다. 이 연구의 목적은 DMCA 기법의 작동원리를 소개하고 국내 유역에 시범적으로 적용해 보는 것이다. 따라서 이 연구에서는 1개 유역과 1개 강우관측소를 사용하였다는 점, 강우자료와 유출자료의 사전 보정이 주관적으로 진행되었다는 점 등의 한계점이 존재한다. 향후 국내 대다수 계측유역에 대한 분석결과를 이용하여 기존의 도달시간 공식들의 대상유역별 특성을 규명함으로써 유역별 적정 도달시간의 범위를 제안할 필요가 있으며, 궁극적으로 미계측유역에서의 도달시간 산정을 위한 대안을 도출할 필요가 있다.
-
Estimating time of concentration by DMCA method
-
Research Article
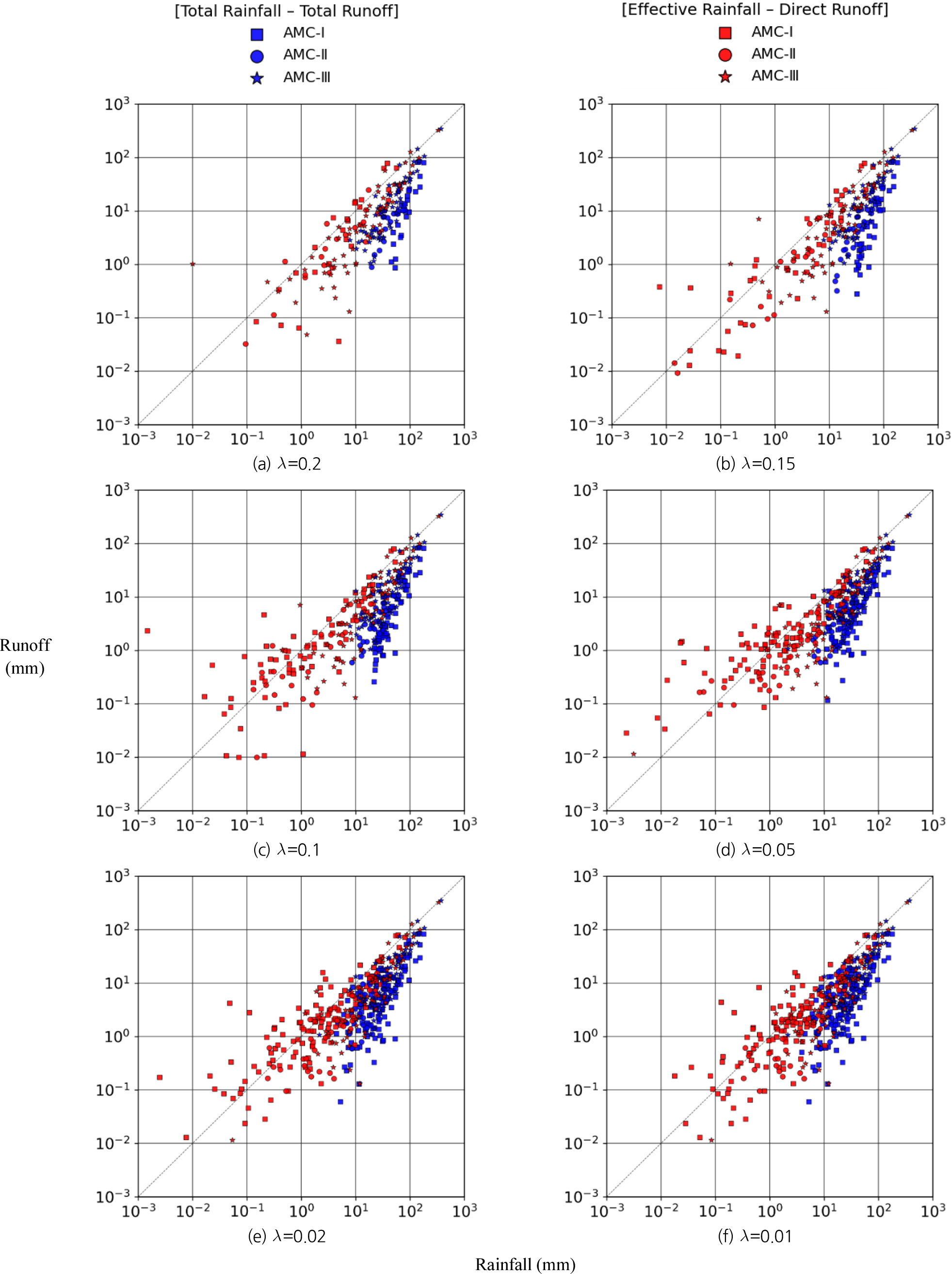
-
Comparative analysis of rainfall-runoff correlation for improving streamflow prediction accuracy
하천 유량 예측 정확성 향상을 위한 강우-유출 상관성 비교 분석
-
Kim, DongkyuㆍKang, MinhyukㆍMin, KyoungwonㆍLee, GyuminㆍKang, Doosun
김동규, 강민혁, 민경원, 이규민, 강두선
- Forecasting streamflow is essential for preparedness against flash floods triggered by intense rainfall and for establishing reliable early-warning systems. Streamflow is primarily …
하천 유량의 예측은 집중 호우에 의한 돌발 홍수에 대비하고 조기 경보 체계를 구축하기 위해 필수적이다. 하천 유량은 주로 유역 내 강우에 의해 …
- Forecasting streamflow is essential for preparedness against flash floods triggered by intense rainfall and for establishing reliable early-warning systems. Streamflow is primarily influenced by rainfall within watershed, which has led to the development of various streamflow prediction techniques. Conventionally, streamflow prediction has been preformed using total rainfall and total runoff data. However, this approach has some limitations in that it includes rainfall events on dry soil or that do not substantially contribute to runoff. In this study, we attempted to investigate more suitable data for streamflow prediction by performing correlation analysis for total rainfall-total runoff sets and effective rainfall-direct runoff events. As a result, the effective rainfall-direct runoff combination relatively achieved higher correlation coefficients and lower error metrics (RMSE, MAE) compared to the total rainfall-total runoff combination, indicating it could improve the accuracy of streamflow prediction. Furthermore, the initial loss ratio and antecedent soil moisture conditions exerted significant control on both the correlation structure and error magnitude. In this study, we investigated the potential of using effective rainfall-direct runoff sets to improve the reliability of streamflow prediction. The findings are expected to contribute to the future development of data-driven river flow prediction models.
- COLLAPSE
하천 유량의 예측은 집중 호우에 의한 돌발 홍수에 대비하고 조기 경보 체계를 구축하기 위해 필수적이다. 하천 유량은 주로 유역 내 강우에 의해 영향을 받으며, 이를 기반으로 다양한 유량 예측 기법들이 개발되어 왔다. 기존의 유량 예측은 총강우-총유출 자료를 활용하여 수행되어 왔으나, 유출에 실질적 영향을 미치지 않는 소규모 강우나 건조한 토양에 내린 강우까지 포함됨으로써 유량 예측 정확성이 저하되는 한계가 존재하였다. 본 연구에서는 총강우-총유출과 유효강우-직접유출의 상관성 분석을 각각 수행하여 하천 유량 예측에 보다 적합한 조합을 평가하고자 하였다. 분석 결과, 유효강우-직접유출 조합이 총강우-총유출 조합에 비해 상대적으로 높은 상관계수와 낮은 오차 지표(RMSE, MAE)를 보여, 하천 유량 예측의 정확도를 향상시킬 수 있을 것으로 판단하였다. 또한, 강우의 초기 손실률과 선행토양함수조건은 상관 구조와 오차 크기에 중요한 영향을 미치는 요인으로 나타났다. 본 연구에서는 하천 유량 예측의 신뢰도를 제고할 수 있는 방안으로 유효강우–직접유출 자료의 활용 가능성을 검토하였으며, 향후 데이터 기반의 하천 유량 예측 모형 개발에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Comparative analysis of rainfall-runoff correlation for improving streamflow prediction accuracy
-
Research Article

-
Assessment of anomaly detection capability of InSAR time-series techniques: A case study of the Jangcheon embankment failure on the Nakdong River
낙동강 장천제 붕괴 사례를 통한 InSAR 시계열 기법의 이상 탐지 가능성 평가
-
Jung, Se JungㆍLee, Du HanㆍKim, Ji Sung
정세정, 이두한, 김지성
- The increasing frequency of extreme rainfall events due to climate change has revealed the limitations of conventional inspection-based structural safety assessments. This …
기후변화로 인한 극한강수의 증가로 기존 점검 기반 구조물 안전 진단의 한계가 드러나고 있다. 본 연구는 2020년 8월에 붕괴된 경상남도 창녕군에 위치한 낙동강 …
- The increasing frequency of extreme rainfall events due to climate change has revealed the limitations of conventional inspection-based structural safety assessments. This study evaluates the potential of InSAR time-series techniques for early anomaly detection, using the case of the Jangcheon Embankment on the Nakdong River in Changnyeong-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do, which collapsed in 2020 August. Under identical conditions, Sentinel-1 SAR imagery was processed using PS-InSAR, PS+DS-InSAR, and E-SBAS methods for comparative analysis. The spatial distribution of scatterers and time-series displacement patterns were examined, and quantitative comparisons were conducted through correlation analysis between cumulative displacement and displacement rate, median-based risk classification, and K-means clustering of displacement types. The results indicate that PS-based approaches are well-suited for high-precision detection centered on the structure, whereas E-SBAS effectively secured stable points even beyond the structural footprint and sensitively detected long-term subsidence trends. Notably, a consistent subsidence response was observed in embankment sections without prior structural presence, suggesting the feasibility of early anomaly detection and the identification of potentially hazardous areas outside the main structure. Based on these findings, this study demonstrates that a multi-method InSAR comparison enables precise delineation of risk zones and provides empirical evidence for the design of early warning and wide-area monitoring systems.
- COLLAPSE
기후변화로 인한 극한강수의 증가로 기존 점검 기반 구조물 안전 진단의 한계가 드러나고 있다. 본 연구는 2020년 8월에 붕괴된 경상남도 창녕군에 위치한 낙동강 장천제를 사례로 Sentinel-1 SAR 영상을 이용해 PS-InSAR, PS+DS-InSAR, E-SBAS 기법을 동일 조건에서 적용·비교하여 구조물 전조 탐지 가능성을 평가하였다. 각 기법의 산란체 분포와 시계열 변위 패턴을 분석하고 누적 변위와 변위 속도 간 상관관계, 중앙값 기반 위험도 분류, K-means 클러스터링을 수행해 변위 유형을 정량적으로 비교하였다. 분석 결과 PS 기반 기법은 구조물 중심의 고정밀 감지에 적합했으며 E-SBAS는 구조물 외곽에서도 안정적인 포인트를 확보하고 장기 침하 추세를 민감하게 탐지하였다. 특히 구조물이 존재하지 않았던 제방 구간에서 나타난 일관된 침하 반응은 전조 탐지 가능성을 시사하며 구조물 외곽의 잠재 위험 지역을 사전에 식별할 수 있음을 보여준다. 이러한 결과를 토대로 본 연구는 다중 InSAR 기법 비교를 통해 위험 구간을 정밀하게 파악하고 조기 경보와 광역 모니터링 체계 설계에 필요한 실증적 근거를 제시한다.
-
Assessment of anomaly detection capability of InSAR time-series techniques: A case study of the Jangcheon embankment failure on the Nakdong River
-
Research Article
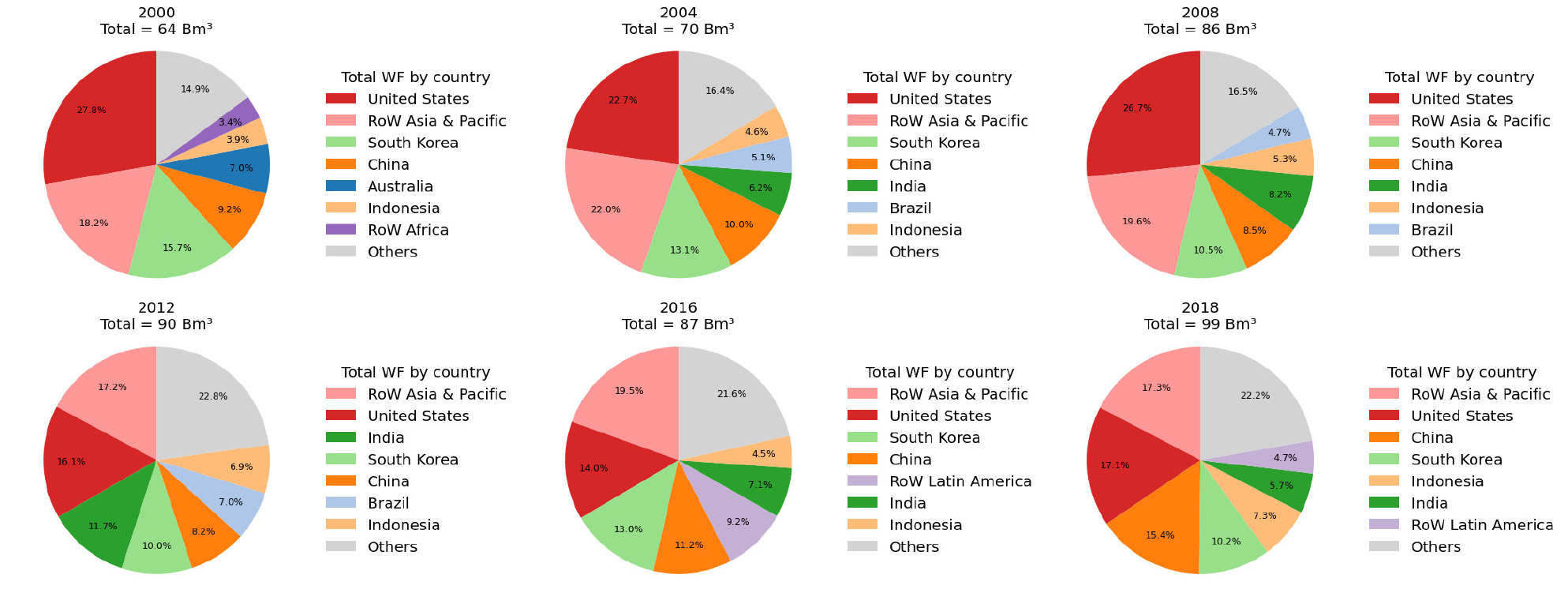
-
South Korea’s dependency on global agricultural sectors and supply shock impacts: A multi-regional input-output analysis
다지역 투입산출분석을 통한 한국의 해외 농업 의존도 및 공급 충격 영향 평가
-
Kim, Daeha
김대하
- Global agricultural trade embodies significant flows of “virtual water,” implying that production shocks in exporting countries may propagate to importing economies as …
세계 농산물 교역은 막대한 규모의 ‘가상수(virtual water)’를 내포하고 있으며, 이는 수출국에서 발생한 생산 충격이 수입국으로 전이되어 식량 및 물 안보 위험으로 이어질 …
- Global agricultural trade embodies significant flows of “virtual water,” implying that production shocks in exporting countries may propagate to importing economies as water and food security risks. South Korea, with limited arable land and water resources, has long relied on grain imports, making it highly exposed to external agricultural and climatic shocks. This study aims to quantify South Korea’s dependency on foreign agricultural sectors and assess the economic impacts of production shocks transmitted through global supply chains. We applied an Environmentally-Extended Multi-Regional Input-Output (EE-MRIO) model combined with the Hypothetical Extraction Method (HEM) to the EXIOBASE3 database for six time periods during 2000-2018. The analysis shows that South Korea’s final demand induced 21.3-29.6 B EUR of global agricultural value added and 64-99 Bm3 of water footprints, with a declining domestic contribution and increasing shares from China, the United States, and Latin America. Sectoral decomposition reveals strong linkages not only with agriculture and food processing but also with services and manufacturing such as textiles. Scenario simulations indicate that a 25% reduction in South Korea’s own agricultural output would decrease national GDP by -0.23%, whereas similar shocks in the United States (-0.025%) or China (-0.006%) produced much smaller effects. These findings highlight that South Korea is structurally vulnerable to domestic agricultural shocks while simultaneously exerting significant demand-side pressures on global water resources, underscoring the need for integrated strategies linking food security, water management, and trade policy.
- COLLAPSE
세계 농산물 교역은 막대한 규모의 ‘가상수(virtual water)’를 내포하고 있으며, 이는 수출국에서 발생한 생산 충격이 수입국으로 전이되어 식량 및 물 안보 위험으로 이어질 수 있음을 의미한다. 국토와 수자원이 제한적인 한국은 곡물 수입에 장기간 의존해 왔기 때문에 외부 농업 및 기후 충격에 구조적으로 취약하다. 본 연구는 한국의 해외 농업부문 의존도를 정량화하고, 글로벌 공급망을 통해 전이되는 생산 충격이 한국 경제에 미치는 영향을 평가하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 이를 위해 2000-2018년 여섯 시점을 대상으로 EXIOBASE3 데이터베이스에 환경확장 다지역 투입산출(Environmentally-Extended Multi-Regional Input-Output, EE-MRIO) 모형과 가상제거법(Hypothetical Extraction Method, HEM)을 적용하였다. 분석 결과, 한국의 최종수요는 전 세계 농업부문에서 연간 21.3 B EUR의 부가가치와 99 Bm³의 물발자국을 유발하였으며, 국내 기여는 감소한 반면 중국, 미국, 라틴아메리카의 비중은 확대되었다. 산업별 분해 결과, 농업 및 식품가공 뿐만 아니라 섬유 등 제조업과 서비스업까지 긴밀히 연결되어 있음이 확인되었다. 또한 HEM 시나리오 분석에서 한국 농업 생산이 25% 감소할 경우 GDP는 -0.23% 감소했으나, 동일한 충격을 미국(-0.025 %)이나 중국(-0.006%)에 적용했을 때는 훨씬 작은 효과만 나타났다. 이러한 결과는 한국이 국내 농업 충격에는 구조적으로 취약한 동시에, 글로벌 수자원에 상당한 수요 기반 압력을 가하고 있음을 보여주며, 식량 안보·물 관리·무역 정책을 연계한 통합적 전략의 필요성을 강조한다.
-
South Korea’s dependency on global agricultural sectors and supply shock impacts: A multi-regional input-output analysis
-
Research Article

-
A study on real-time object detection-based disaster type recognition and classification
실시간 객체 인식 기반 재난 유형 탐지 및 분류에 관한 연구
-
Lee, YejinㆍNam, Su HanㆍKim, Sung EunㆍKim, Young Do
이예진, 남수한, 김성은, 김영도
- Disasters occur in diverse and unpredictable forms, underscoring the necessity of rapid initial response. Citizen-reported images captured via smartphones provide a valuable …
재난은 자연적 또는 인위적 요인으로 인해 예측이 어렵게 발생하며, 복합적 양상으로 확대되어 심각한 피해를 초래한다. 이러한 재난 상황에서 신속하고 정확한 탐지는 피해 …
- Disasters occur in diverse and unpredictable forms, underscoring the necessity of rapid initial response. Citizen-reported images captured via smartphones provide a valuable means of acquiring disaster scene information without temporal or spatial constraints; however, the risk of misinformation necessitates careful verification. This study developed a YOLOv8-based object detection model to detect and classify six disaster types forest fire, vehicle fire, building fire, pothole, road crack, and flood using citizen-reported images. The dataset was collected, preprocessed, and augmented, and transfer learning was applied to optimize model performance. Evaluation was conducted through cross-validation and an independent test dataset, yielding strong results with Precision = 0.956, Recall = 0.937, mAP@0.5 = 0.964, and mAP@0.5-0.95 = 0.792. The model achieved excellent performance in fire- and flood-related categories, while relatively lower performance was observed for forest fire and road crack due to similarities in color and texture with the background. The proposed model improves the reliability and timeliness of image-based disaster detection and classification, contributing to the advancement of early disaster response and management systems. Furthermore, it supports the verification of citizen-reported images, reducing false detections caused by misinformation, and provides a foundation for building standardized disaster image databases and developing intelligent disaster management systems.
- COLLAPSE
재난은 자연적 또는 인위적 요인으로 인해 예측이 어렵게 발생하며, 복합적 양상으로 확대되어 심각한 피해를 초래한다. 이러한 재난 상황에서 신속하고 정확한 탐지는 피해 최소화를 위한 초기 대응의 핵심 요소이다. 본 연구에서는 6종 재난 유형을 탐지·분류할 수 있는 YOLOv8 기반 객체 탐지 모델을 개발하였다. 수집된 이미지를 전처리하고 애노테이션을 수행한 후, 다양한 이미지 증강(image augmentation) 기법을 적용하여 모델의 일반화 성능을 강화하였다. 성능 평가 결과 Precision = 0.956, Recall = 0.937, mAP@0.5 = 0.964, mAP@0.5–0.95 = 0.792로 높은 탐지 정확도를 보였다. 특히 화재 및 홍수 관련 재난에서 우수한 성능을 나타냈으나, 산불화재 및 도로균열처럼 배경과 색상·질감이 유사한 객체에서는 상대적으로 낮은 탐지율을 보였다. 제안된 모델은 다양한 환경에서도 신속하고 정확한 재난 탐지 및 분류가 가능한 고성능 프레임워크를 제시하였으며, 향후 시민제보, 드론 영상, CCTV 영상 등 실시간 영상 데이터와 연계한 재난 대응 및 관리 체계의 고도화에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
A study on real-time object detection-based disaster type recognition and classification
-
Research Article / 우수학생논문상
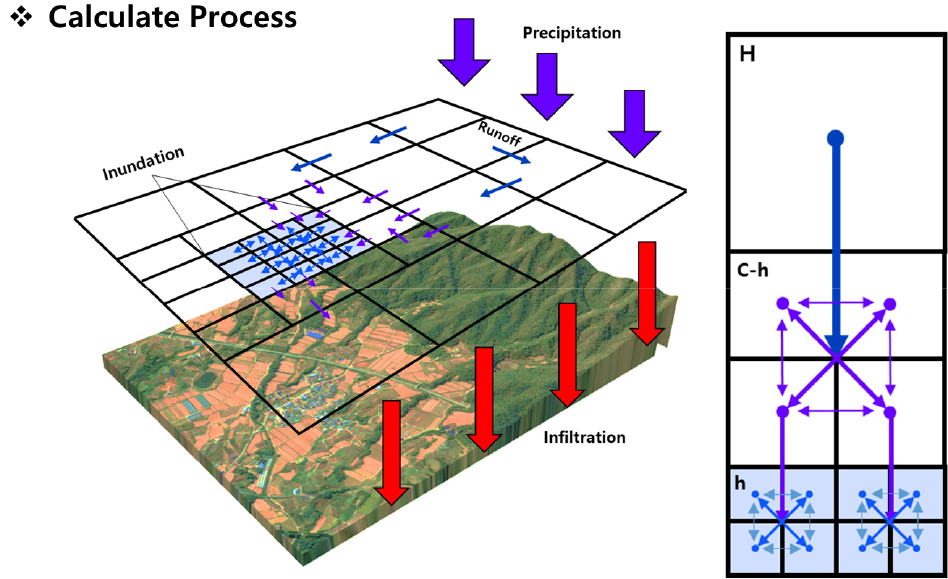
-
Validation of a large-scale rainfall-runoff-flood model for the Seomjin River basin
대유역 강우 유출-범람 모형의 섬진강 유역 적용성 검토
-
Ku, HeonsungㆍAn, HyunukㆍKang, Hansol
구현승, 안현욱, 강한솔
- This study validated a large-scale integrated rainfall-runoff-inundation model through its application to the Seomjin River Basin, which experienced a significant flood event …
본 연구에선 2020년 8월 대규모 홍수가 발생한 섬진강 유역을 대상으로 대유역 통합형 강우 유출-범람 모형의 적용성 검토를 수행하였다. 모형은 1D Kinematic wave …
- This study validated a large-scale integrated rainfall-runoff-inundation model through its application to the Seomjin River Basin, which experienced a significant flood event in August 2020. The model simultaneously simulates hydrological rainfall-runoff processes using the one-dimensional kinematic wave equation and hydraulic flood inundation using the two-dimensional shallow water equation, while incorporating an Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) scheme to improve computational efficiency at the basin scale. In addition, the Thiessen polygon method was applied to distribute rainfall spatially, and the model was designed to account for reservoir releases, which are essential in large-scale flood inundation analysis. For this purpose, outflow data from four major dams in the basin were collected and used to establish two simulation scenarios depending on whether dam releases were included. The simulation results indicated that, when dam releases were considered, the model reproduced more than 89% of the observed inundation areas across all regions, and discharge validation at major bridge stations showed a coefficient of determination (R2) of up to 0.92, successfully capturing peak discharge timing and flow variations. These findings demonstrate the model’s capability for large-scale flood inundation analysis, and it is expected that further improvements through the incorporation of more detailed flow processes and parameter calibration will enhance its potential use in flood disaster prevention and management.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에선 2020년 8월 대규모 홍수가 발생한 섬진강 유역을 대상으로 대유역 통합형 강우 유출-범람 모형의 적용성 검토를 수행하였다. 모형은 1D Kinematic wave Eq을 사용한 수문학적 강우 유출 현상과 2D shallow water Eq을 사용한 수리학적 흐름 해석 및 침수계산을 동시에 수행하며, 유역 단위 분석에서 계산 효율성 향상을 위하여 적응형 격자 세분화 기법(Adaptive Mesh Refinement; AMR)을 도입하였다. 또한 Thiessen 알고리즘을 적용하여 강우를 공간적으로 분포시키며, 대유역 범람 해석이라는 특수성을 고려해 댐 방류량을 적용한 계산이 가능하도록 설계되었다. 이에 본 연구의 경우 섬진강 유역 4개 주요 댐 방류량을 수집하였으며 자료 반영 여부에 따라 두 가지 시나리오로 구분하여 모의를 수행하였다. 모의 결과 댐 방류량 적용 시 침수 면적은 관측 침수 피해 면적 대비 전 구역에서 89% 이상을 재현하며, 주요 교량 지점에서 수행한 유출량 검증에서 R2가 최대 0.92로 계산되어 첨두 유량 발생 시점과 유량 변동 패턴을 우수하게 재현하는 것으로 확인되었다. 이를 통하여 모형의 대유역 범람 해석 능력이 검증되었으며 추후 실제 유동 현상 알고리즘화 적용 및 매개변수 조절 등을 통한 모형의 고도화로 향후 홍수 재해 예방 및 대응책 마련에 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Validation of a large-scale rainfall-runoff-flood model for the Seomjin River basin
-
Research Article

-
Assessment of flood risk in agricultural land under extreme rainfall events
극한강우 발생시 농경지 홍수 위험도 평가
-
Deepak, ChaulagainㆍAdisa, Hammed AkinsojiㆍChoi, Kyung Sook
디팍차우라가인, 아디사하메드 아킨소지, 최경숙
- Climate change has increased the frequency and intensity of extreme rainfall, resulting in recurrent agricultural flooding. This study evaluates flood-prone agricultural zones …
최근 기후변화로 인한 극한강우의 빈도와 강도가 증가하면서 농경지 홍수 재해가 반복적으로 발생하고 있다. 본 연구는 강우 재현기간 및 최대가능강수량(PMP) 분석을 기반으로 충청남도 …
- Climate change has increased the frequency and intensity of extreme rainfall, resulting in recurrent agricultural flooding. This study evaluates flood-prone agricultural zones in South Chungcheong Province by applying rainfall return period analysis and probable maximum precipitation (PMP) to assess the impact of inadequate drainage capacity. The results indicate that northern areas such as Asan and Cheonan, and southern and southwestern regions including Boryeong, Seocheon, Buyeo, and Hongseong, are highly vulnerable to extreme rainfall. The PMP analysis further identifies Boryeong, Seocheon, Buyeo, and Cheongyang as critical hotspots of flood risk associated with extreme rainfall in South Chungcheong Province. Approximately 23% of the agricultural land falls within the very high and 16% within the high flood-risk category, with paddy fields being the most vulnerable, followed by upland croplands and mixed vegetation. These findings provide practical insights for improving drainage infrastructure and developing adaptive strategies to ensure agricultural resilience under changing climate conditions.
- COLLAPSE
최근 기후변화로 인한 극한강우의 빈도와 강도가 증가하면서 농경지 홍수 재해가 반복적으로 발생하고 있다. 본 연구는 강우 재현기간 및 최대가능강수량(PMP) 분석을 기반으로 충청남도 농경지 지역의 배수능력 부족으로 야기되는 농경지 침수가능 취약지역을 평가하였다. 그 결과, 아산과 천안지역을 포함한 충남 북부 지역과 보령, 서천, 부여, 홍성지역을 포함한 충남 남부 및 남서부 지역이 극한 강우에 매우 취약한 것으로 평가되었다. PMP 분석을 통해, 충남지역 극한강우 발생시 보령, 서천, 부여, 청양지역이 특히 홍수재해 발생 위험이 매우 높은 지역으로 확인되었다. 농경지 홍수위험 등급 분석에서는 전체 농경지의 약 23%가 매우 높은 위험 등급, 16%가 높은 위험 등급에 각각 속하는 것으로 나타났다. 또한 농경지 유형 중에서 논이 가장 홍수에 취약한 것으로 평가되었으며, 그 다음으로 밭, 혼합 초지 순으로 홍수에 취약한 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구 결과는 농경지 배수시설의 개선과 농업분야 기후변화 적응전략 수립에 실질적인 시사점을 제공할 것으로 사료된다.
-
Assessment of flood risk in agricultural land under extreme rainfall events
-
Special Issue: 지능형 도시홍수 예측
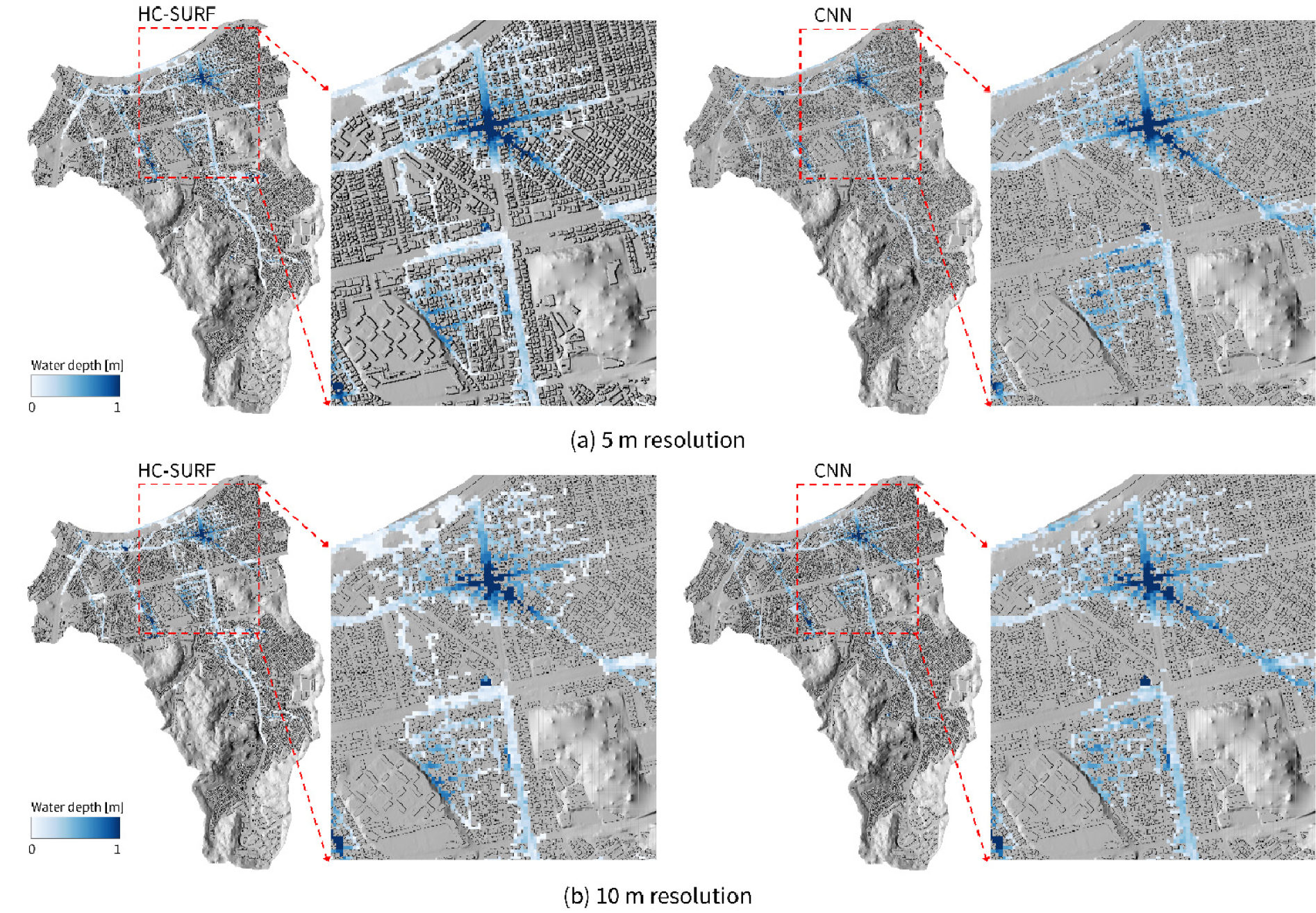
-
Urban inundation prediction with an HC-SURF-Trained Gated-CNN surrogate: The Sillim drainage district case study
HC‑SURF 물리모형 정보 연계 Gated‑CNN 기반 도시 침수 예측: 신림 배수분구 사례
-
Woo, HyunaㆍSim, Sang BoㆍKim, Hyung-JunㆍKim, HakseongㆍNoh, Seong Jin
우현아, 심상보, 김형준, 김학성, 노성진
- Physics-based urban inundation models yield reliable results under limited observations but are constrained by computational cost for real-time use. This study develops …
도시 지역에서 물리 기반 침수 해석 모형은 관측 자료가 부족한 상황에서도 신뢰성 있는 결과를 제공하지만, 높은 계산 비용으로 인해 실시간 적용에는 한계가 …
- Physics-based urban inundation models yield reliable results under limited observations but are constrained by computational cost for real-time use. This study develops a Gated-Convolutional Neural Network (Gated-CNN) deep learning model trained on HC-SURF (Hyper Connected Solution for Urban Flood) simulations and quantitatively evaluates how spatial resolution (5 m, 10 m) affects predictive performance. For the August 2022 event in the Sillim drainage district (Seoul), the 5 m model achieved CSI 0.78 and R² 0.89, whereas the 10 m model delivered higher overall accuracy and stability (CSI 0.82, R²0.90). Depth-specific analysis indicated comparable skill in shallow water (<0.15 m) and lower error in deep water (≥1.0 m) for the 10 m model (RMSE 0.34 m vs 0.53 m at 5 m). Inference for a 6 h event was about 65 times faster than the physics-based model (16 s vs 1,041 s), supporting suitability for real-time operation. These results can serve as reference data for selecting spatial resolution and for developing real-time urban flood forecasting systems.
- COLLAPSE
도시 지역에서 물리 기반 침수 해석 모형은 관측 자료가 부족한 상황에서도 신뢰성 있는 결과를 제공하지만, 높은 계산 비용으로 인해 실시간 적용에는 한계가 있다. 본 연구에서는 HC-SURF 물리모형 정보를 활용해 학습한 Gated-Convolutional Neural Network (Gated-CNN) 기반 딥러닝 모형을 구축하고, 공간 해상도(5 m, 10 m)가 성능에 미치는 영향을 평가하였다. 서울 신림 배수분구의 2022년 8월 침수 사상에 대한 검증 결과, 딥러닝 모형은 5 m 해상도에서 CSI 0.78과 R² 0.89를 보였으며, 10 m 해상도에서는 CSI 0.82와 R² 0.90으로 성능이 향상되었다. 침수심 구간별 분석에서는 얕은 구간(<0.15 m)에서 두 해상도의 성능이 유사했으나, 깊은 구간(≥1.0 m)에서는 10 m 모형의 RMSE (0.34 m)가 5 m 모형(0.53 m)보다 낮았다. 또한 딥러닝 추론 시간은 물리모형 대비 약 65배 단축되어(평균 16초 vs 1,041초), 실시간 운영에 적합한 계산 효율성을 확인하였다. 본 연구는 도시 침수 예측 모형의 해상도 선택과 실시간 예보 체계 구축을 위한 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
Urban inundation prediction with an HC-SURF-Trained Gated-CNN surrogate: The Sillim drainage district case study
-
Special Issue: 지능형 도시홍수 예측
-
Integrating observed and simulated inundation data for urban flood hazard mapping via Indicator Cokriging
지점 관측 및 공간모의 침수 정보를 연계한 Indicator Cokriging 기반 도시침수 위험도 산정 기법
-
Kim, MinyoungㆍChoi, HyeonjinㆍKim, BomiㆍSong, Chang GeunㆍNoh, Seong Jin
김민영, 최현진, 김보미, 송창근, 노성진
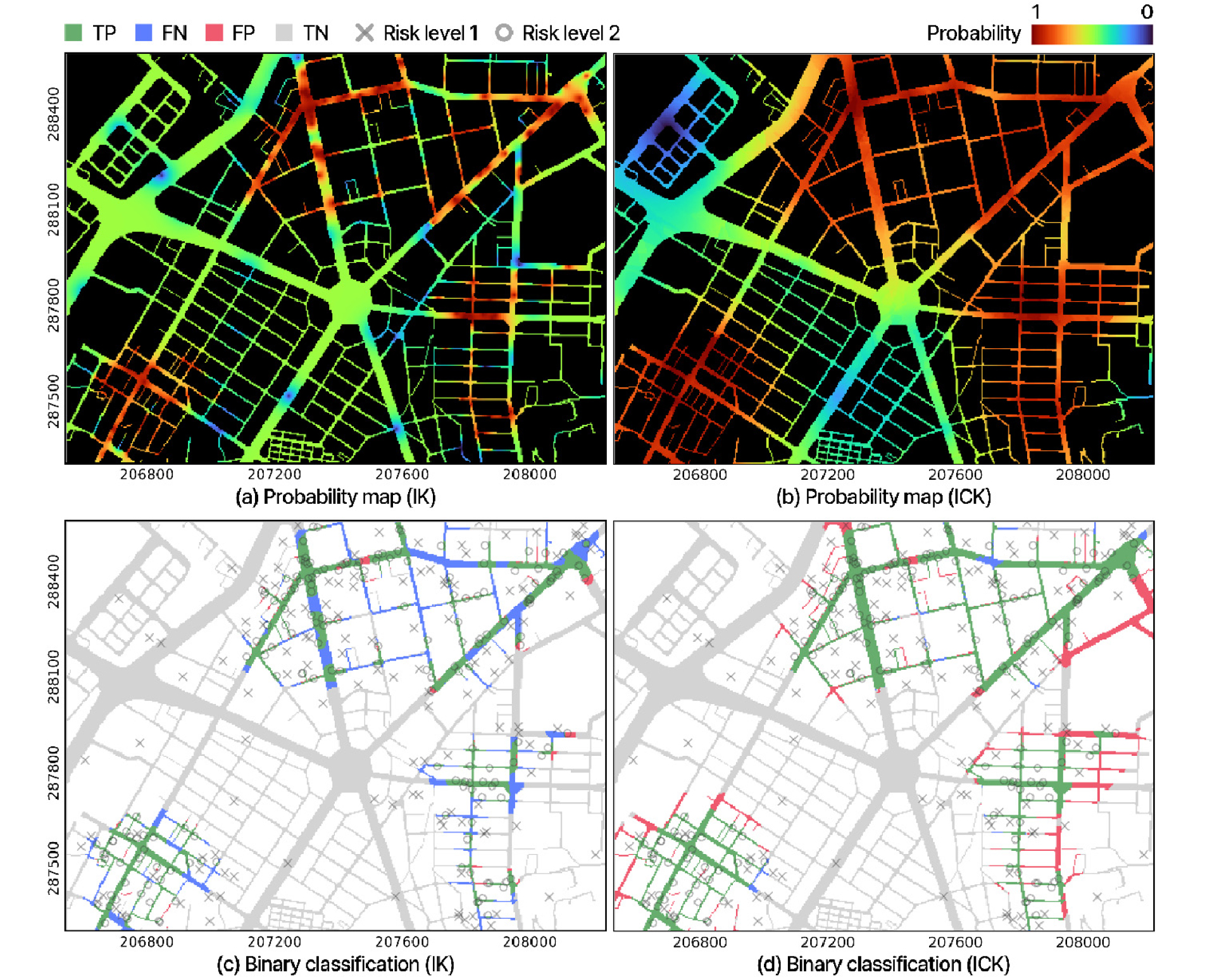
- This study presents an urban flood hazard mapping approach that integrates observed inundation data with model-simulated results via Indicator Cokriging (ICK). Observed …
본 연구는 Indicator Cokriging (ICK) 기법을 이용하여 지점 관측 자료와 공간 모의 자료를 효과적으로 통합하는 도시 침수 위험도 산정 방법을 제안한다. 제안된 …
- This study presents an urban flood hazard mapping approach that integrates observed inundation data with model-simulated results via Indicator Cokriging (ICK). Observed inundation serves as the primary variable, while hydrologic factors, including simulated maximum inundation depth from a physics-based model and distance to the inundation boundary, are incorporated as secondary variables to characterize spatial correlation structures. This study aims to develop a framework of probabilistic mapping that accounts for spatial dependence among observations and cross-correlation between heterogeneous datasets. Synthetic experiments in the Oncheon-cheon catchment in Busan evaluated robustness to varying observation densities and rainfall uncertainty. Relative to Indicator Kriging (IK), ICK improved the F1-score by up to 21.6%, accuracy by up to 10.3%, and the normalized Matthews correlation coefficient by up to 13.6%, with gains increasing as observation density rose. Rainfall-uncertainty tests confirmed stable performance (AUC ≥ 0.86) across scenarios scaled to 75-200% of baseline rainfall. The proposed framework provides a reliable means to enhance urban flood hazard maps by effectively integrating observed and simulated data.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 Indicator Cokriging (ICK) 기법을 이용하여 지점 관측 자료와 공간 모의 자료를 효과적으로 통합하는 도시 침수 위험도 산정 방법을 제안한다. 제안된 방법론은 침수 관측 정보를 주요변수로 설정하고, 물리 기반 모형의 모의 침수심과 침수 경계로부터의 거리 등 수문학적 인자들을 보조변수로 활용하여 공간적 상관구조를 추정한다. 이를 통해 관측점 간 공간적 의존성과 서로 다른 자료들 간의 교차 상관성을 동시에 고려하는 확률론적 도시침수 공간 위험도 추정 체계를 구축하였다. 부산 온천천 유역에 대한 합성 실험을 통해 합성 관측 밀도와 강우 불확실성에 대한 위험도 추정의 안정성을 정량적으로 평가하였으며, ICK 기법의 보조변수들이 도시침수 위험도 산정에 미치는 기여도를 검증하기 위해 Indicator Kriging (IK) 기법과의 비교분석을 수행하였다. ICK 기법은 IK 기법 대비 F1-score 최대 21.6%, ACC 최대 10.3%, nMCC 최대 13.6% 향상되었으며, 관측점 밀도 증가에 따른 예측 정확도의 일관된 개선을 확인하였다. 강우 불확실성 분석에서는 기준 강우량 대비 75~200%의 범위에서도 모형성능(AUC ≥ 0.86)이 안정적으로 유지되었다. 제안된 체계는 관측 정보를 활용한 침수 공간정보 신뢰성 향상에 기여할 것으로 기대된다.
-
Integrating observed and simulated inundation data for urban flood hazard mapping via Indicator Cokriging
-
Special Issue: 지능형 도시홍수 예측
-
Development of two-dimensional finite volume flow model with edge-based hydrostatic reconstruction and its application to urban flood
엣지 기반 정수압 재구성 2차원 유한체적 흐름 모형 개발 및 도시 홍수 적용
-
Shin, Eun TaekㆍRhee, Dong SopㆍEum, Tae SooㆍSong, Chang Geun
신은택, 이동섭, 엄태수, 송창근
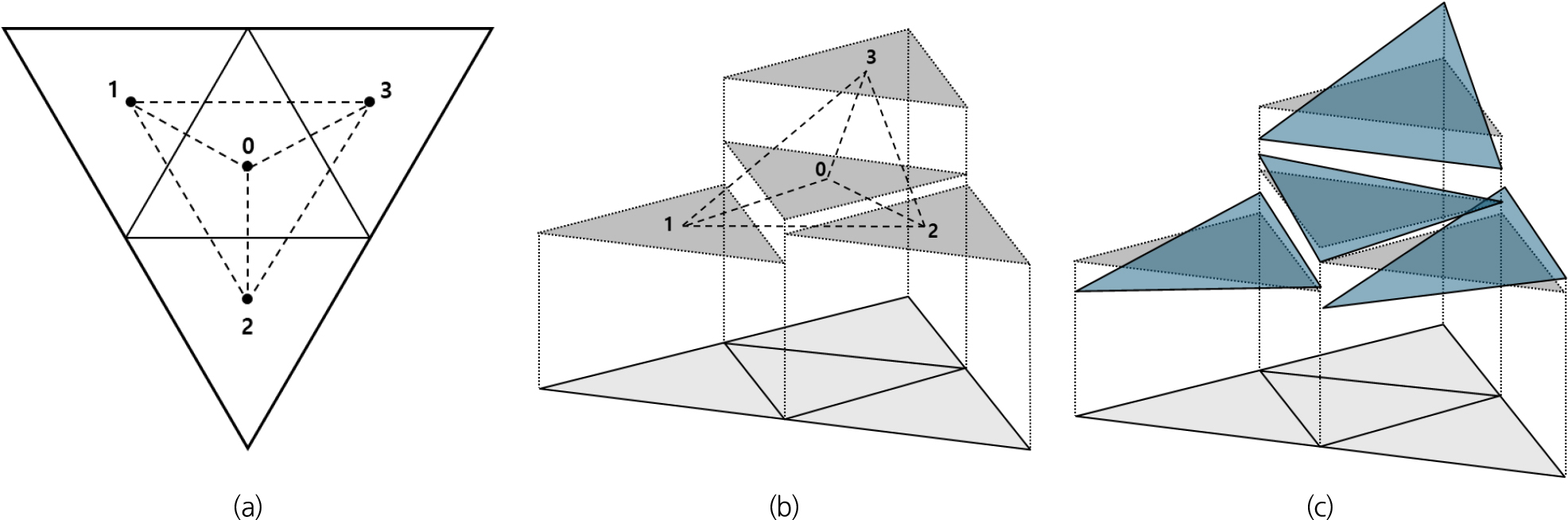
- This study developed a two-dimensional finite volume flow model with edge-based hydrostatic reconstruction for accurate and stable simulation of flash floods in …
본 연구에서는 복잡한 도시 지형에서 발생하는 돌발 홍수를 정확하고 안정적으로 모의하기 위하여 엣지 기반 정수압 재구성 기법을 적용한 2차원 유한체적 흐름해석 모형을 …
- This study developed a two-dimensional finite volume flow model with edge-based hydrostatic reconstruction for accurate and stable simulation of flash floods in complex urban environments. The proposed model incorporates MUSCL slope limiting and the HLLC approximate Riemann solver on unstructured triangular cells and employs a well-balanced scheme to maintain the equilibrium between flux and source terms, thereby satisfying the C-property. To enhance numerical stability and computational efficiency for large-scale urban flood simulations, implicit friction treatment and a high-performance parallel computing framework (Taichi) were implemented. The model performance was verified through benchmark tests, including Toro’s Riemann problems and Thacker’s planar solution, demonstrating its capability to capture shock propagation and wetting-drying transitions. The model was further applied to the 2007 Pasha Bulker storm event in Newcastle, Australia, and validated against experimental data as well as results from FLUMEN and HDM-2D models. The analysis confirmed that the proposed model successfully reproduced key urban flood characteristics, such as water depth rise in front of buildings and flow acceleration through narrow passages. Quantitative comparisons at 13 measurement points showed errors comparable to or lower than those of the existing models.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 복잡한 도시 지형에서 발생하는 돌발 홍수를 정확하고 안정적으로 모의하기 위하여 엣지 기반 정수압 재구성 기법을 적용한 2차원 유한체적 흐름해석 모형을 개발하였다. 개발된 모형은 비구조 삼각 격자에서 MUSCL 경사 제한과 HLLC 근사 리만 솔버를 결합하고, 보존항과 소스항의 균형을 유지하는 well-balanced 기법을 적용하여 C-속성을 만족하도록 구현되었다. 또한, 마찰항의 음해적 처리와 고속 병렬 연산 프레임워크(Taichi)를 도입하여 대규모 도시 홍수 해석에서의 수치적 안정성과 계산 효율성을 확보하였다. 모형의 성능은 Toro의 Riemann 문제와 Thacker의 곡면 회전 문제와 같은 검증 예제를 통해 충격파 전파와 마름-젖음 경계 처리 능력을 확인하였다. 2007년 ‘Pasha Bulker’ 폭풍으로 피해를 입은 호주 뉴캐슬 지역을 대상으로 적용하였으며, 실험 결과 및 기존 모형(FLUMEN, HDM-2D)과 비교·검증하였다. 분석 결과, 건물 전면부 수위 상승, 협소 통로에서의 병목 현상 등 도시 홍수 특성이 정확히 재현되었으며, 13개 검증 지점에서 수심 및 유속 오차는 기존 모형과 유사하거나 일부 구간에서는 더 낮게 나타났다.
-
Development of two-dimensional finite volume flow model with edge-based hydrostatic reconstruction and its application to urban flood
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association